Shoeing for Chronic Laminitis
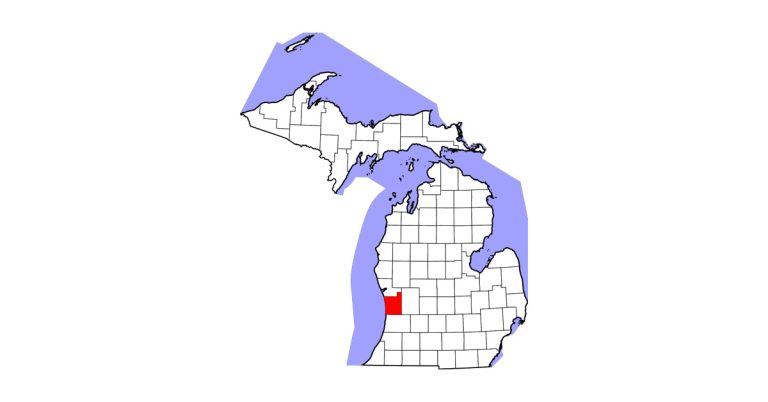
There are limited options for effective treatment of horses with lameness due to chronic laminitis. A common practice involves therapeutic shoeing, which is intended to reduce pain, aid in healing, and help return the horse to activity. Recently, researchers from Texas A&M University examined four types of therapeutic shoes to determine their effectiveness at rapidly reducing pain and