International Equine Disease Report, First Quarter 2015
Reported diseases include equine herpesvirus, strangles, equine viral arteritis, contagious equine metritis, and more
Reported diseases include equine herpesvirus, strangles, equine viral arteritis, contagious equine metritis, and more

Long-distance travel has potential complications for horses including colic, injury, and shipping fever.

Infections can be reduced by recognizing the risk and having appropriate cleaning, disinfection, and hygiene protocols.
Early recognition of emerging and re-emerging diseases is of paramount importance if their impact is to be minimized.

Renal (kidney) disease and acute kidney injury with other disease processes can increase morbidity and mortality.
Diseases diagnosed include herpesvirus, tetanus, strangles, piroplasmosis, West Nile virus, and more.

Horses have been one of the signature sectors of Kentucky’s agricultural economy for many years.

What’s the difference between heaves, COPD, RAO, and equine asthma? Dr. Laurent Couetil explains.
Learn about polymerase chain reaction assays, how they work, and how veterinarians interpret their results.

A laboratory test is only as good as the sample submitted. Find out how veterinarians submit samples.

One researcher explains why he believes a central repository is needed for equine gene expression information.
Diagnosed diseases include strangles, influenza, vesicular stomatitis, hendra virus, salmonellosis, and more.

Despite all that is known, important questions still remain about wobbler syndrome.

One veterinarian shares her thoughts on what West Nile virus can teach us about exotic equine diseases.
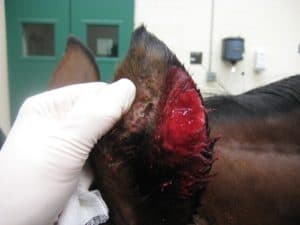
In horses, leishmaniasis presents as nodules on the head, pinnae, scrotum, legs, and neck–the areas where sand flies commonly feed. These nodules can occur in groups or be solitary, and they often ulcerate.
Learn about pythiosis, a disease characterized by ulcerative, granulomatous lesions on and beneath horses’ skin.
Stay on top of the most recent Horse Health news with