
Deltamethrin for Culicoides, AHS Control Studied
Researchers found that the insecticide deltamethrin did not appear to prevent midges from feeding on horses.


Researchers found that the insecticide deltamethrin did not appear to prevent midges from feeding on horses.

Retained placenta, lochiometra, and injuries to the perineum were the most common puerperal (after birthing) issues.

Laser resection resulted in reduced postoperative complications and a positive prognosis, researchers determined.

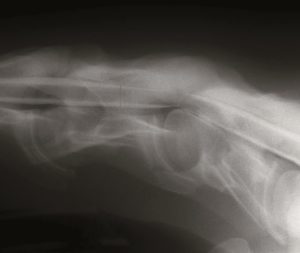
Temporohyoid osteoarthropathy (THO) can cause vestibular nerve damage and balance problems in affected horses.

Transport-associated fever is a common issue that can disrupt training schedules or indicate infection.
For the most part, the adverse reactions were mild and self-limiting. But some serious ones did occur.

Some forelimb lamenesses can result in the horse appearing unsound in a hind limb.

Researchers found that, overall, 90.5% of mares and 82.3% of foals survived to hospital discharge following treatment.
Using a new test, researchers determined that bloodworms are associated with nonstrangulating intestinal infarctions.

Horses can develop signs of toxicity soon after eating the plant or its seeds, but residual signs can persist for weeks.

Horses undergoing multiple colic surgeries in a 14-day period are at greater risk for incisional infections.

Infrared thermography (IRT) appears effective at measuring a horse’s skin temperature during water treadmill exercise.

Reducing the prevalence of catastrophic equine injuries and sudden deaths could help improve jockey safety.
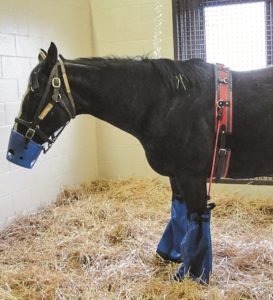
Methods that immerse the hoof and limb in ice and water to at least fetlock level are most effective.

More than 56% of injuries occurred in the right forelimb, the opposite of what’s most commonly seen in Thoroughbreds.

Researchers found that 82% of surgically managed horses and 61% of medically managed horses survived a cecal impaction.
Stay on top of the most recent Horse Health news with