International Equine Disease Report, First Quarter 2017
Confirmed diseases include influenza, EHV, strangles, nocardioform placentitis, piroplasmosis, EIA, and more.
Confirmed diseases include influenza, EHV, strangles, nocardioform placentitis, piroplasmosis, EIA, and more.

Genetic and genomic research could help veterinarians diagnose disease early and select more targeted treatments.

Find tips on managing and preventing a “perfect storm” of infectious disease spread at horse competition facilities.

Find out how veterinarians diagnose this highly contagious disease in both acute cases and long-term carrier horses.

Learn about several substances that can cause heart muscle damage and death in horses.

Anthelmintic resistance occurs worldwide. With only three drug classes to choose from, are we running out of options?

In the past, researchers developed new classes of antiparasitic compounds every 10 years or so. But what works today?
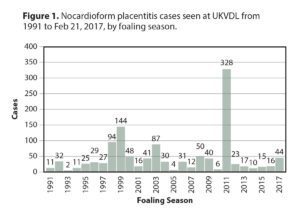
Through the third week of February, 44 cases of nocardioform placentitis were confirmed in the 2017 Kentucky foal crop.

Digestive system and cardiovascular system problems were the most common causes of death in the study population.
Confirmed diseases include equine herpesvirus, West Nile virus, African horse sickness, strangles, influenza, and more.

Although maggots typically pose little serious threat to hosts, screwworms are a separate and often dire exception.

Coronavirus is associated with disease outbreaks in adult horses in Japan and the United States. Learn more.

One researcher describes the promising progress that’s been made in lameness diagnosis and treatment.

Vets can glean crucial information by evaluating horses with performance issues in hand, on the longe, and under saddle.
Diseases reported include African horse sickness, influenza, EHV, EIA, rabies, and more.

Genomic tools could help address horse health problems that couldn’t be resolved with earlier technologies.
Stay on top of the most recent Horse Health news with